Revolutionizing Color Precision and Energy Efficiency in Entertainment Lighting
As stage lighting technology continues to evolve, lighting designers are constantly seeking solutions that provide greater color accuracy, increased energy efficiency, and compact fixture designs. In this pursuit, Quantum Dot LED (QD-LED) technology has emerged as a game-changer, promising enhanced color purity and control far beyond what conventional white-light LED systems can deliver.
This article explores how Quantum Dot LED technology works, its advantages over traditional systems, and its potential applications in professional stage lighting environments.
1. What Is Quantum Dot LED Technology?
Quantum dots are nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit light when stimulated by energy. Their most revolutionary property is that they emit specific wavelengths depending on their size—smaller particles emit blue light, while larger ones emit red. This precise control over color generation allows for narrow, vivid spectral output not possible with traditional phosphor-based LEDs.
In a QD-LED lighting system, blue LEDs provide the excitation source, and the light passes through a quantum dot layer. Each dot absorbs the blue light and re-emits it in a defined color (e.g., red or green). By combining red, green, and blue emissions, the system produces full-spectrum white light—or any mix of rich, saturated colors.
2. How Quantum Dot LEDs Improve Stage Lighting
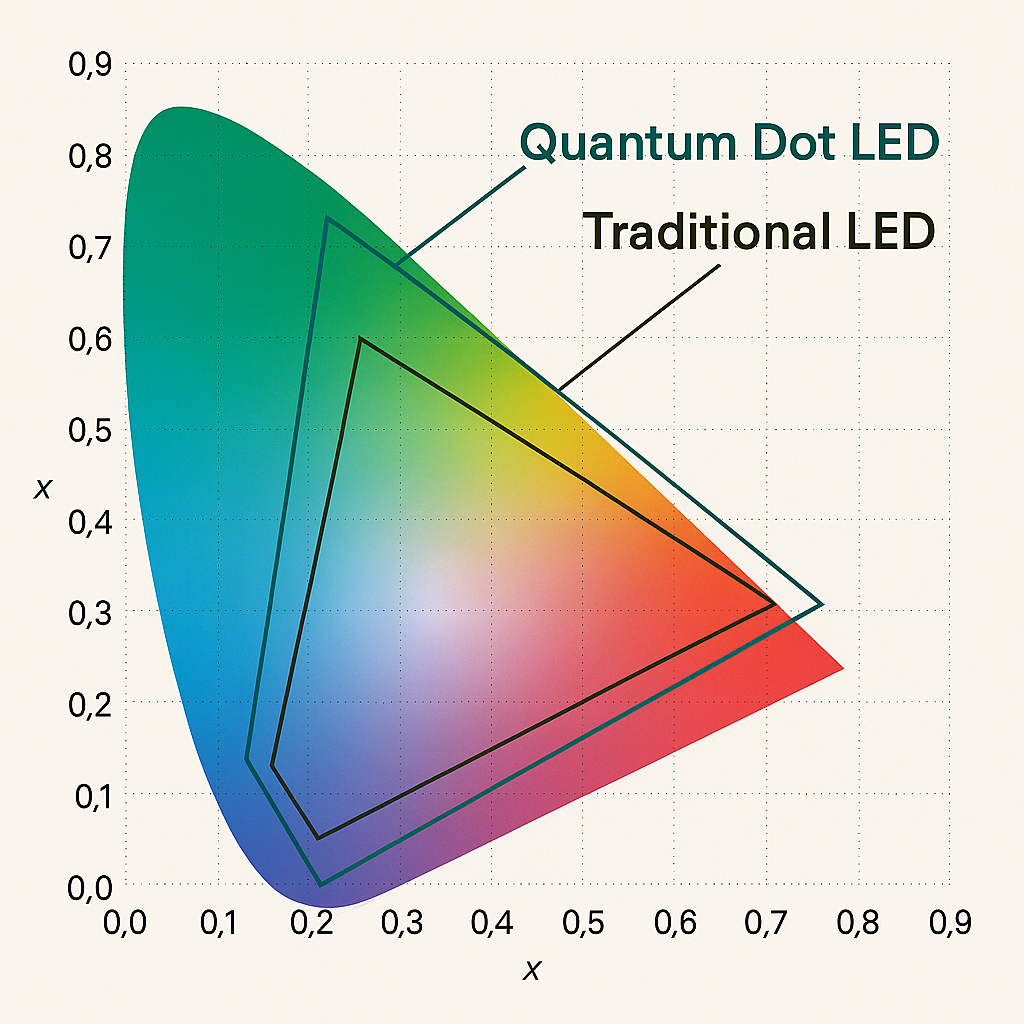
A. Spectral Accuracy and Color Gamut
Stage designers often struggle with matching lighting colors across different mediums—video walls, costumes, skin tones, scenic painting, etc. Traditional LEDs have broader spectral peaks, leading to washed-out or inaccurate colors under certain conditions.
Quantum Dot LEDs provide a significantly narrower spectral profile, allowing much more accurate rendering of primary and secondary colors. This is crucial when precise color matching is required, such as in:
Theatrical lighting
Cinematic stage setups
Broadcast television studios
Fashion runways
B. Higher Color Rendering Index (CRI)
Typical white LEDs (phosphor-converted) often cap around CRI 80–85. Quantum Dot-enhanced systems can easily achieve CRI 95 or higher, producing light that more closely replicates natural daylight. This leads to better visual comfort and more vibrant scene realism.
C. Energy Efficiency
While Quantum Dot LEDs are still advancing in output-per-watt metrics, their precise spectral control means less energy is wasted as non-visible heat or irrelevant frequencies. Stage environments that need long runtimes or portable fixtures (e.g., festival trusses or touring rigs) stand to benefit from lower power consumption and reduced cooling requirements.
D. Consistency and Longevity
Because quantum dots don’t degrade like phosphors and their materials are more chemically stable, QD-LED fixtures maintain their spectral characteristics over time. This is especially beneficial for venues with fixed installations where relamping or recalibration is costly or logistically difficult.
3. Applications in Stage Lighting
Though still an emerging field, QD-LEDs are already being prototyped or tested in several entertainment scenarios:
| Application Type | Quantum Dot LED Advantage |
|---|---|
| Theatrical Spotlighting | True-to-life skin tone reproduction under colored scenes |
| Architectural Projection | Better control over tone and gradient without digital correction |
| Studio and Film Lighting | High CRI improves post-production accuracy |
| Touring Stage Rigs | Lightweight units, lower energy draw, excellent color stability |
As LED fixture formats become more modular, it’s likely that many moving heads, pars, and wash lights will integrate quantum dot layers or hybridized systems in the near future.

4. Comparison: QD-LED vs Traditional LED
| Feature | Traditional White LED | Quantum Dot LED |
|---|---|---|
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | ~80–85 | 90–98+ |
| Spectral Width | Broad peaks | Narrowband, precise emission |
| Power Efficiency | High (some heat loss) | Potentially higher |
| Lifespan | 25,000–50,000 hrs | Similar or longer |
| Color Saturation | Moderate | Very high |
While cost is currently higher, prices are expected to fall as demand and production scale rise.
5. Challenges and Limitations
Quantum Dot LEDs still face some barriers to widespread adoption:
Cost: Quantum dot materials, especially cadmium-free variants, are expensive to produce at scale.
Integration: Existing lighting console systems may need firmware updates or calibration protocols to handle the narrower band outputs effectively.
Output Intensity: Some QD-LEDs lag behind phosphor LEDs in raw lumen output, though this is improving.
However, many manufacturers are investing heavily in refining these issues, with several patents and production lines aimed specifically at entertainment-grade lighting solutions.
6. Future Outlook: Hybrid Fixtures and AI Color Control
One of the most exciting developments is the potential for hybrid fixtures: combining Quantum Dot emitters with traditional RGBW or RGBACL arrays, allowing users to switch between high-output and ultra-precise modes.
Additionally, as AI-based lighting control systems evolve, pairing them with Quantum Dot LED engines can yield real-time color correction, responsive scene transitions, and even ambient color matching based on sensor input.
As quantum dot manufacturing scales up and control ecosystems catch up, stage lighting could soon shift from wide-spectrum approximation to pure, digitally-defined photonics.
READ MORE:





Blue Sea Lighting is an enterprise with rich experience in the integration of industry and trade in stage lighting and stage special effects related equipment. Its products include moving head lights, par lights, wall washer lights, logo gobo projector lights, power distributor, stage effects such as electronic fireworks machines, snow machines, smoke bubble machines, and related accessories such as light clamps.
Quick Links
For more questions subscribe to our email








